Bomb Calorimeter Calculator
This calculator can be used to verify and make the necessary calculations regarding heat release from a calorimeter. You can understand the relation that governs the heat release and temperature change inside it.
How the Bomb Calorimeter Works
The bomb calorimeter is a device used to measure the energy released by the combustion of a substance. It provides accurate data on the heat of combustion, which is essential in chemistry, nutrition, and energy studies.
Steps to Use the Bomb Calorimeter
- Place a known quantity of the sample into the calorimeter's container.
- Fill the calorimeter bomb with oxygen to ensure complete combustion.
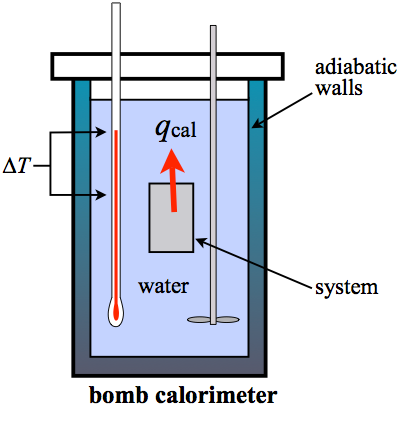
- Submerge the bomb in a water jacket equipped with a temperature sensor.
- Ignite the sample using the built-in electrical ignition system.
- Record the temperature rise in the surrounding water to calculate the heat released.
Calculating Heat of Combustion
The main formulas used are:
1. Heat Released (Q)
Q = m × C × ΔT
- Q = heat released in Joules (J)
- m = mass of water (kg)
- C = specific heat capacity of water (J/kg·°C)
- ΔT = temperature change of water (°C)
2. Heat of Combustion (ΔHcomb)
ΔHcomb = Q / msample
- ΔHcomb = heat of combustion per gram of sample (J/g)
- msample = mass of the substance burned (g)
Example 1: Combustion of Glucose
Suppose we burn 2 grams of glucose (C6H12O6) in the calorimeter. If the water surrounding the bomb has a mass of 1 kg, specific heat capacity 4.18 J/g°C, and temperature rises by 5°C:
- Q = 1 × 4.18 × 5 = 20.9 kJ
- ΔHcomb = 20.9 kJ / 2 g = 10.45 kJ/g
This value indicates the energy content per gram of glucose.
Example 2: Combustion of Octane
Now, we burn 1.5 g of octane (C8H18) under similar conditions. If the water temperature rises by 8°C:
- Q = 1 × 4.18 × 8 = 33.44 kJ
- ΔHcomb = 33.44 kJ / 1.5 g = 22.29 kJ/g
Octane releases more energy per gram compared to glucose, which aligns with its use as a fuel.
Common Substances and Their Heat of Combustion
| Substance | Heat of Combustion (J/g) |
|---|---|
| Octane (C8H18) | 47.7 |
| Glucose (C6H12O6) | 15.6 |
| Hydrogen | 141.8 |
| Methane (CH4) | 55.5 |
Understanding Results
The bomb calorimeter allows precise measurement of the energy released. High ΔHcomb values indicate substances with higher energy content. This information is vital for fuel analysis, food energy calculations, and chemical experiments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the purpose of a bomb calorimeter?
It measures the heat released during combustion to determine the energy content of a sample. Useful for fuels, food, and chemical analysis.
2. Can any material be tested?
Yes, but the sample must fit in the bomb and be compatible with complete combustion.
3. How is it different from a simple calorimeter?
A bomb calorimeter operates at high pressure in a sealed container, ensuring complete combustion and accurate results. Simple calorimeters are less controlled.
4. How is ΔHcomb derived?
By dividing the heat absorbed by the water (Q) by the mass of the sample burned.
5. What types of substances are commonly tested?
Fuels (gasoline, methane), foods (carbohydrates, fats), and other chemical materials.
Explore More Tools
Check our collection of Thermodynamics calculators: Flame Temperature Calculator, Ionization Energy Calculator, Phase Change Calculator